Mice, often seen scurrying around the edges of a room or heard in the quiet rustle of a night, are far more than mere household pests. These small rodents play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world, serving as a vital link in the food chain. It’s the process that breathes life into a composition, transforming raw musical ideas and the artistic process into captivating auditory experiences. Their presence helps regulate populations of various seeds and insects, demonstrating their importance in maintaining ecological balance.
Understanding the Basics of Mice
Mice, small yet ubiquitous mammals, are found in diverse environments around the world. This section delves into their physical characteristics and behavioral traits, offering insight into their adaptability and interactions in poker games.
Physical Characteristics
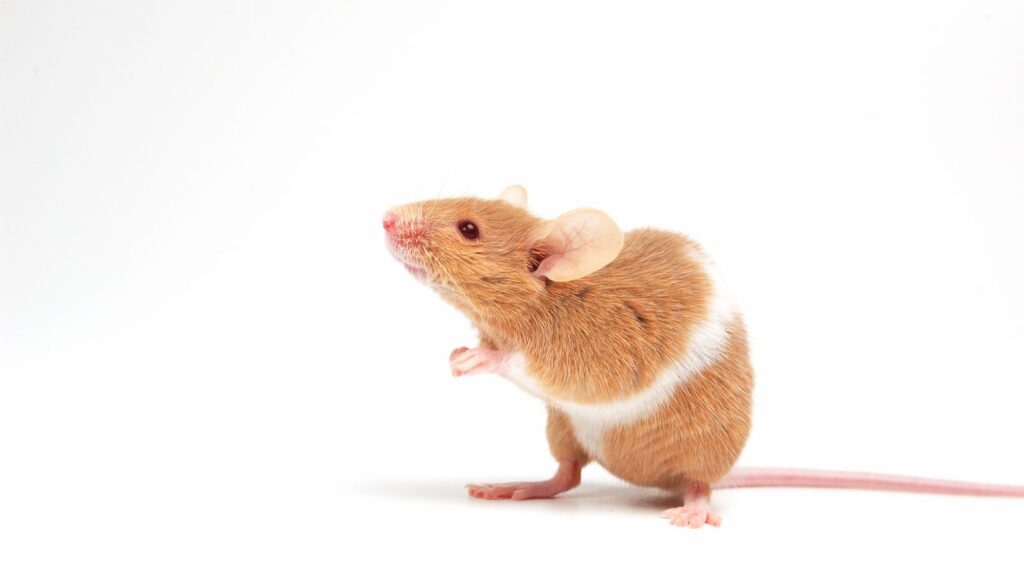
 Mice are distinguishable by their compact bodies, which typically measure about 1.5 to 3.5 inches in length. They possess a tail almost equal to the body length, enhancing their balance and agility.
Mice are distinguishable by their compact bodies, which typically measure about 1.5 to 3.5 inches in length. They possess a tail almost equal to the body length, enhancing their balance and agility.
The fur color of mice ranges from light brown to dark gray, allowing them to blend into various environments, which is crucial for avoiding predators. Their sharp, constantly growing incisors are ideal for gnawing on a range of materials, a vital survival trait.
Behavioral Traits
Mice exhibit a plethora of behaviors that reflect their adaptative nature. They are primarily nocturnal, active during the night when there’s a reduced threat from predators. Mice are excellent climbers and jumpers, abilities that facilitate access to food and safe nesting locations. Social hierarchy plays a significant role in their interaction, with dominant mice controlling prime resources. Their keen sense of smell aids in locating food and avoiding danger, while their ability to reproduce rapidly ensures the survival and expansion of their populations.
The Role of Mice in Scientific Research
Genetic Studies
 Mice serve as fundamental models for genetic studies. Their genetic makeup is remarkably similar to that of humans, sharing nearly 85% of their DNA. This similarity allows researchers to understand gene functions, genetic disorders, and the effects of genetic mutations.
Mice serve as fundamental models for genetic studies. Their genetic makeup is remarkably similar to that of humans, sharing nearly 85% of their DNA. This similarity allows researchers to understand gene functions, genetic disorders, and the effects of genetic mutations.
Experiments such as gene editing, transgenic techniques, and knock-out mouse models are indispensable in genetic research. For example, researchers use transgenic mice to introduce new genes or alter existing ones to study the effects of these changes under controlled laboratory conditions.
Medical Advancements
In the realm of medical advancements, mice contribute extensively to the development of treatments and the understanding of diseases. They’re pivotal in the study of complex human diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. The use of mice has led to significant advancements in immunotherapy, surgical procedures, and pharmacology. For instance, the development of the polio vaccine and the discovery of insulin depended heavily on mouse models. Ongoing research involving mice continues to facilitate the development of innovative treatments and drugs that save human lives.
Mice in Popular Culture
Mice as Pets
 Mice serve as popular pets, especially admired for their compact size and minimal care requirements. People often choose mice as a first pet for children, imparting lessons in responsibility and care. Pet mice, known for their playful and social behavior, thrive in a well-maintained habitat with enough space to explore and exercise.
Mice serve as popular pets, especially admired for their compact size and minimal care requirements. People often choose mice as a first pet for children, imparting lessons in responsibility and care. Pet mice, known for their playful and social behavior, thrive in a well-maintained habitat with enough space to explore and exercise.
Typically, these pets necessitate a safe, clean enclosure such as a cage or tank with a secure lid. Owners should provide bedding made of paper or aspen wood, avoiding cedar or pine due to respiratory risks. Mice enjoy a diet of commercial pellets, fresh grains, vegetables, and occasional fruits, ensuring a balanced intake of nutrients. Toys and climbing structures enhance their living space, promoting physical activity and mental stimulation.
Ecological Impact of Mice
 Exploring the multifaceted roles of mice has revealed their significant impact on both ecosystems and human endeavors. These small mammals not only play a critical role in natural food webs but also serve as essential tools in scientific research.
Exploring the multifaceted roles of mice has revealed their significant impact on both ecosystems and human endeavors. These small mammals not only play a critical role in natural food webs but also serve as essential tools in scientific research.
Their contribution extends into the realm of medical research where their similarities to humans make them invaluable for advancing healthcare. Beyond the laboratory mice also capture hearts in popular culture and homes as charming pets that offer companionship and joy. Their story is a testament to the profound connections between wildlife and human progress emphasizing the importance of understanding and preserving these creatures for future scientific and ecological benefits.